Swedish Realtime Voice Agent
🇸🇪 I made a realtime Swedish conversational AI voice agent.
📌 TL;DR
🇸🇪 How to make an all-Swedish low latency realtime AI voice agent running on Evroc.
- 🔗 Live Demo: https://talktoevroc.olof.tech
- 🔗 Source Code: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc
🎯 Conclusion: Now absolutely doable. "The future has arrived". All technical components available.
✅️ Live Demo!
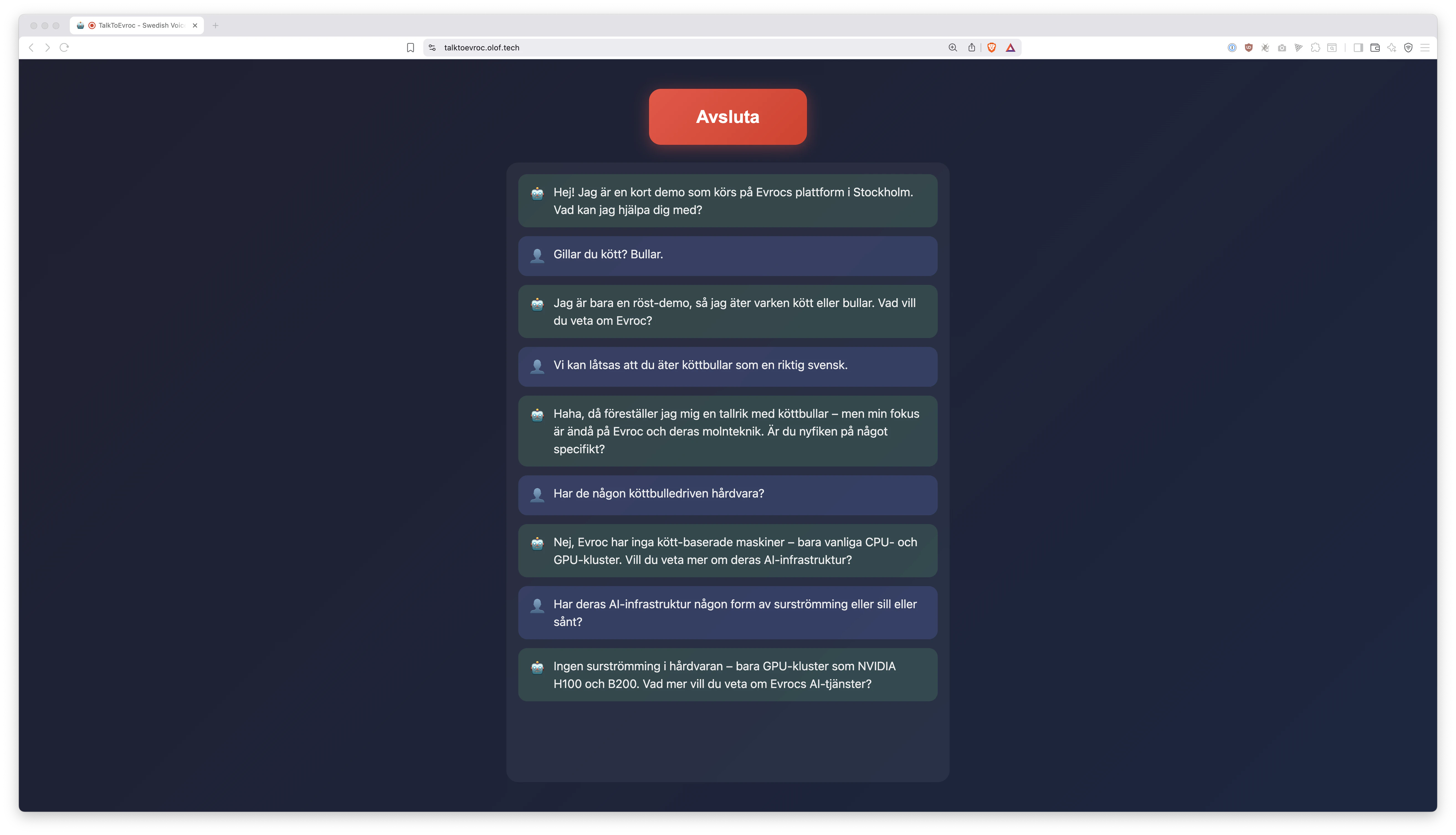
Try it yourself: https://talktoevroc.olof.tech
It puts the rest of this engineering blog post in context.
💪 Let's do something "really hard"!
A great way to have fun and learn new technology is attempting to do something (supposedly) really hard or cutting edge. Just using text based AI might not seem that cutting edge anymore. GPT-3 was released over 5 years ago.
However, I feel like realtime voice based conversational AI still has a bit of that ✨ shiny cutting edge feel to it. Especially if you make it hard for yourself and decide that this AI ...
- ... should understand spoken
Swedish🇸🇪 really well. - ... should answer with a
Swedish🇸🇪 voice. - ... should run in a
Swedish🇸🇪 datacenter. - ... said datacenter must be owned by a
Swedish🇸🇪 company.
I'm a big fan of http://elevenlabs.io. Their voice agent platform works great and is easy to use! It is however expensive 💸 and it leverages the American cloud 🇺🇸.
For sensitive sectors, like healthcare, sending recordings of patient voice to the American cloud may not be a viable option for privacy reasons.
Also: It's never wrong to save some money, right?
As we'll find in this engineering blog post the state of available open source software and AI models makes this supposedly "really hard" challenge easier than expected. 😱
🧩 The parts that make the agent
Simply put a realtime AI voice agent is built with the following components:
- 👂 STT: "Speech to Text" Converts human speech to text. The ears of the AI.
- 🧠 LLM: "Large Language Model" The AI brains. Takes text in and gives text out.
- 🗣️ TTS: "Text to Speech" Converts the text from LLM to spoken audio.
- 📦 Harness: The plumbing that combines three above together.
- 🏛️ Datacenter: The hardware/cloud that runs the above.
- 🖥️ UI: An interface for the user to interact with our AI agent.
😅 Each component above would be terribly hard to make from scratch. Luckily, we'll mostly plug things together. In 2026 we can just carefully pick the right combination of pre-made components that yield great results.
👂 STT: KB Whisper
For Speech to Text we have the magnificent https://huggingface.co/KBLab/kb-whisper-large. The National Library of Sweden is on a roll! This is "Kungliga Bibliotekets" fine tuned version of https://huggingface.co/openai/whisper-large-v3. KBWhisper transcribes Swedish much better overall and also handles Swedish dialects better.
🧠 LLM: GPT-OSS-120B
For LLM we'll use https://huggingface.co/openai/gpt-oss-120b. This is currently the best and largest open weights model released by OpenAI. It understands Swedish pretty well, infers quickly and cheaply thanks to the Mixture of Experts architecture, and is currently commonly offered by AI inference providers. There's also great open weight Chinese AI models available out there, but maybe American feels safer for now?
🗣️ TTS: Piper
To give our AI a voice we'll use https://github.com/OHF-Voice/piper1-gpl. We'll use the Swedish voice https://huggingface.co/rhasspy/piper-voices/tree/main/sv/sv_SE/nst which is also trained by the National Library of Sweden ❤️. Note that Piper infers super quickly and cheaply even on CPU which is the reason I chose it for this project. For a higher quality voice you may want to plug in something like https://github.com/resemble-ai/chatterbox instead.
📦 Harness: PipeCat
We plumb the three above together using https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat. It is an open source harness/framework for realtime conversational AI. I really like how pluggable PipeCat is. The STT, LLM, and TTS components can easily be exchanged.
🏛️ Datacenter: Evroc
We'll run it all on https://evroc.com. Truly a Swedish 🇸🇪 company with Swedish 🇸🇪 datacenter. They are well-stocked on Blackwell GPUs and have a shared/PayGo AI-API offering with the models we need. I'll confess I'm a bit of an Evroc fanboy 😊. More on that later.
🖥️ UI: Simple React + WebSockets
A pretty simple user interface that leverages https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat with WebSocket transport and React. All source code available on GitHub: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc. Note that Pipecat supports a multitude of other transports, such as different telephone providers.
🚀 Overcoming the challenges with Evroc
Did I mention I'm a bit of an Evroc fanboy 😊?
🌟 Latency: To achieve that realtime conversational feel we need low latency every step of the way. Since we are building a Swedish agent the intended users are likely Swedish. Great that the Evroc data center is in Sweden then! Internal latency between each component matters a lot as well. With Evroc we can run it all in the same datacenter. STT, LLM, TTS and Harness all execute within the same Evroc data center meaning latency is as low as it gets. For example: No outbound calls to an overseas American data center, such as OpenAI for LLM. For context rumour is that https://elevenlabs.io recently started experimenting self hosting GPT-OSS-120B on their premises to cut down on latency.
🌟 Inference Speed: Evroc is well stocked on Blackwell GPUs. This is the latest and greatest from NVIDIA. The crazy bastards even run the Whisper STT inference on Blackwell cards 😲. That's overkill but actually helps with realtime voice agents because we get the Whisper transcript back crazy fast. I don't have the exact numbers but we are talking well over a x100 realtime speed factor for transcribing audio.
🌟 Swedish = A Niche Language: Just 0.12% of the world population speaks Swedish. It is a niche language. Compare that to the English language, spoken by about ~19% of the world, and it's no surprise most AI models are much better at English. For the best Swedish results we need to use niche Swedish models, such as KB Whisper, and Evroc has that as part of their shared/PayGo offering which is really convenient.
🌟 Shared Offering: It looks like Evroc is investing significantly into their shared AI-API offering right now. That makes it easy to start using them with low volumes because you pay per use and not capacity. They have a dedicated B200 offering as well but that would be way too expensive for a tech demo like this one.
👨💻 Technical Details
All code is available at https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc. It is MIT Licensed. I encourage you - go ahead and steal with pride for your own projects and endeavors!
🔎 Let us look closer at some interesting technical details and findings I made:
💻 Whole BE in a single short main.py
This is the whole backend: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc/blob/master/main.py
Not much. PipeCat does most work for us! Evroc offers OpenAI compatible APIs so pointing to Evroc is as easy as:
stt = OpenAISTTService(
api_key=EVROC_API_KEY,
base_url=EVROC_BASE_URL,
model="KBLab/kb-whisper-large",
language=Language.SV,
prompt="Evroc, Evrocs, KBLab, NVIDIA, GPU, B200, H100, hyperscale",
)
llm = OpenAILLMService(
api_key=EVROC_API_KEY,
base_url=EVROC_BASE_URL,
model="openai/gpt-oss-120b",
params=BaseOpenAILLMService.InputParams(extra={"reasoning_effort": "low"}),
)
Make sure to use low LLM reasoning effort for snappy answers.
I otherwise leaned heavily on the plenty of examples available at https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-examples.
💻 Deceptively Complex Dockerfile
The Dockerfile looks deceptively complex: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc/blob/master/Dockerfile
This is only because the official PipeCat base Dockerfile does not come prebuilt for macOS and that's what I use for local development.
Just diff it against the https://github.com/daily-co/pipecat-cloud-images/blob/main/pipecat-base/Dockerfile and you will see that it is a slightly modified copy-paste.
💻 Piper Voice
Some minor Dockerfile and entrypoint.sh complexity stems from running the Piper server within the same container. We are basically starting two different servers: our main.py and the Piper server. See: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc/blob/master/piper-start.sh
The --length-scale section speeds up the speech, which I found made for a snappier experience:
# Speech speed factor (1.5 = 50% faster)
# Piper uses length_scale where lower = faster, so we invert: 1/1.5 ≈ 0.67
SPEED_FACTOR=1.5
LENGTH_SCALE=$(awk "BEGIN {printf \"%.3f\", 1 / $SPEED_FACTOR}")
echo "Starting Piper TTS (${SPEED_FACTOR}x speed)..." >&2
uv run python -m piper.http_server \
--host 127.0.0.1 \
--port 5000 \
--length-scale "$LENGTH_SCALE" \
-m "$VOICE_MODEL" >&2 &
And in main.py we compensate for some bad (mostly Swenglish) pronunciation:
PRONUNCIATION_FIXES: dict[str, str] = {
"AI": "äj-aj",
"GPU": "g p u",
"API": "a p i",
"B200": "b två hundra",
"H100": "h ett hundra",
"NVIDIA": "envidia",
...
}
💻 WebSocket Transport
PipeCat recommends WebRTC transport. I used WebSocket instead - why? For WebRTC you need a STUN/TURN server. I did not feel like setting one up myself or searching for a Swedish Sovereign provider as part of this experiment. PipeCat is built by https://www.daily.co and they try to push their paid WebRTC offering, which we don't want to use in this experiment because it is American.
Their premade component https://github.com/pipecat-ai/voice-ui-kit/blob/main/package/src/components/PipecatAppBase.tsx does not support WebSocket out of the box, so the most complex part of the frontend is this version that is modified for WebSocket transport: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc/blob/master/client/src/WebSocketPipecatAppBase.tsx.
The rest of the Frontend is a pretty minimal Bun + Vite + React project.
⛅ Deploying on Evroc
👏 Okay, let's deploy the server on Evroc!
For this we'll use https://kamal-deploy.org. Kamal is way simpler than Kubernetes. It has that Heroku ease of use feeling and works with pretty much any server. As they say themselves "Deploy web apps anywhere. From bare metal to cloud VMs." You can see the Kamal deploy.yml I used here: https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc/blob/master/config/deploy.yml
1️⃣ First, create an API key. You can do this from the "Think > Playground" tab:
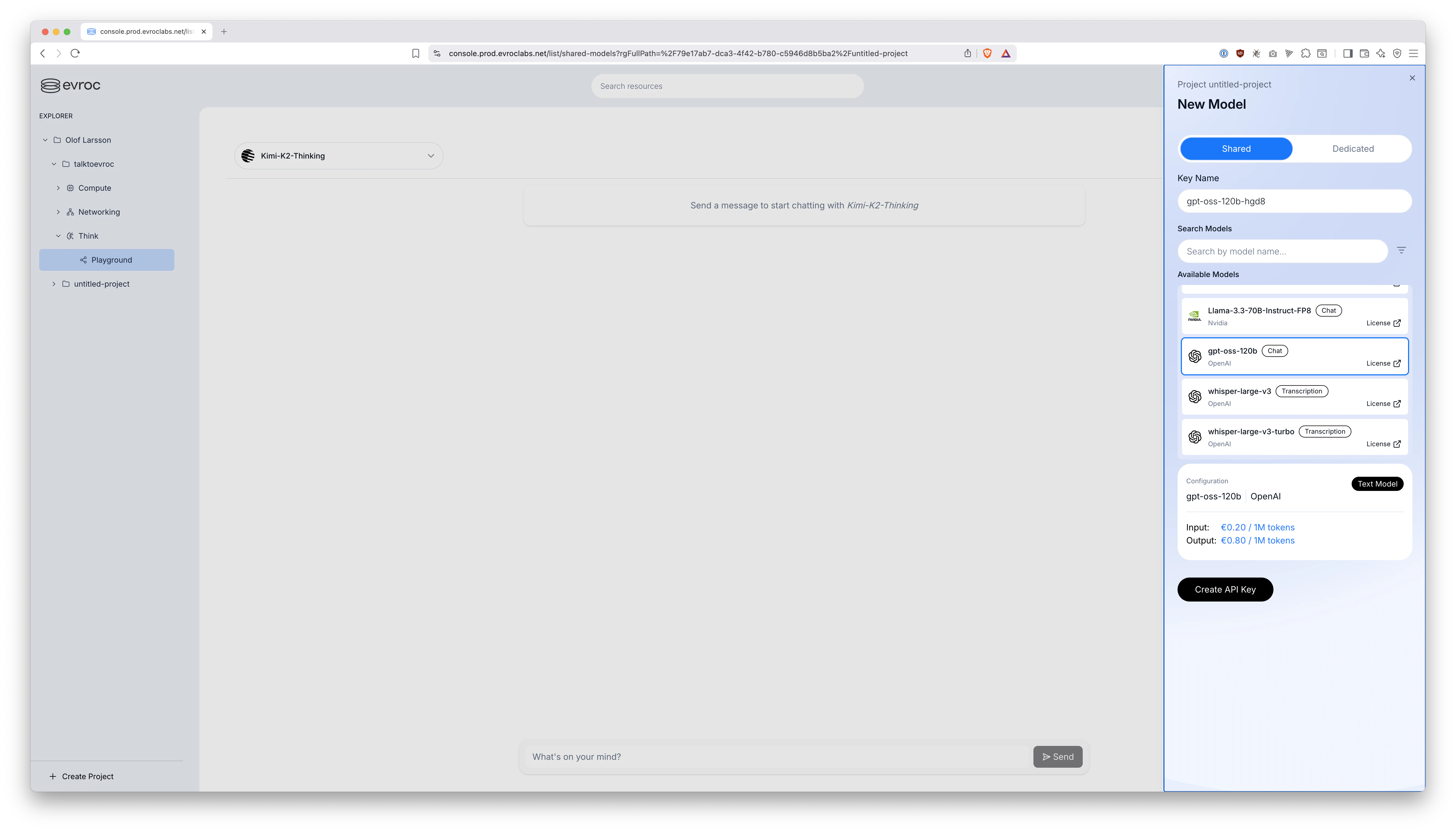
Make sure it is a Shared API Key and not Dedicated.
Apparently which model you select when creating the API key does not actually matter. The one API key will work for all the shared models. So, just create one and it will be the one you use for both STT and LLM workloads.
Set it on your local machine with export EVROC_API_KEY="...".
2️⃣ Next, create a new security group default-sto-1-web that looks like this in the Evroc console:
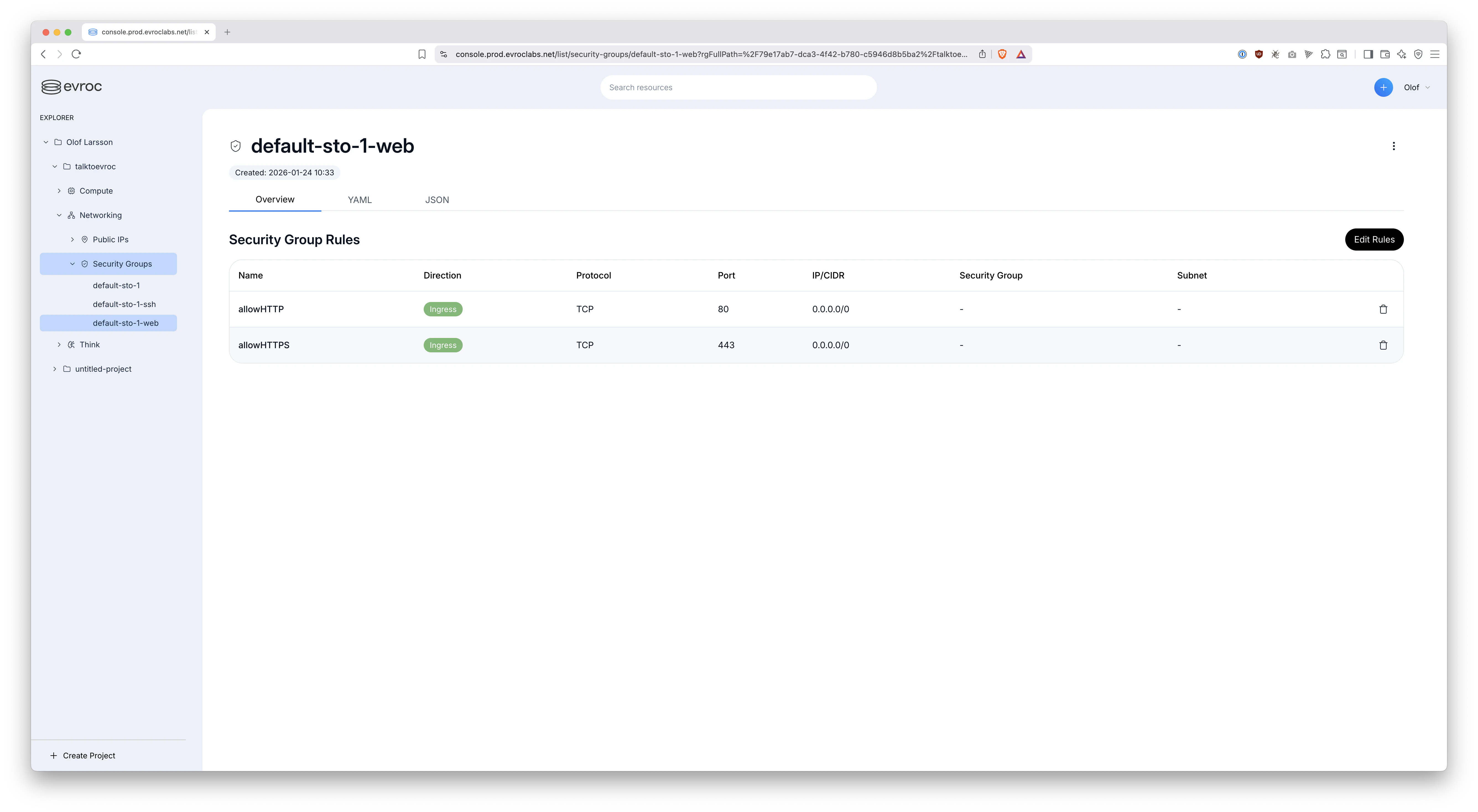
The security groups default-sto-1 and default-sto-1-ssh are created automatically, which is super convenient. But, we'll need to create this new default-sto-1-web manually to allow web traffic in through the firewall. As feedback to Evroc it would be great if such a security group were also created automatically for you.
3️⃣ Now we create a new VM. I just called it talktoevroc and bumped up the CPU core count a little since Piper runs on CPU:
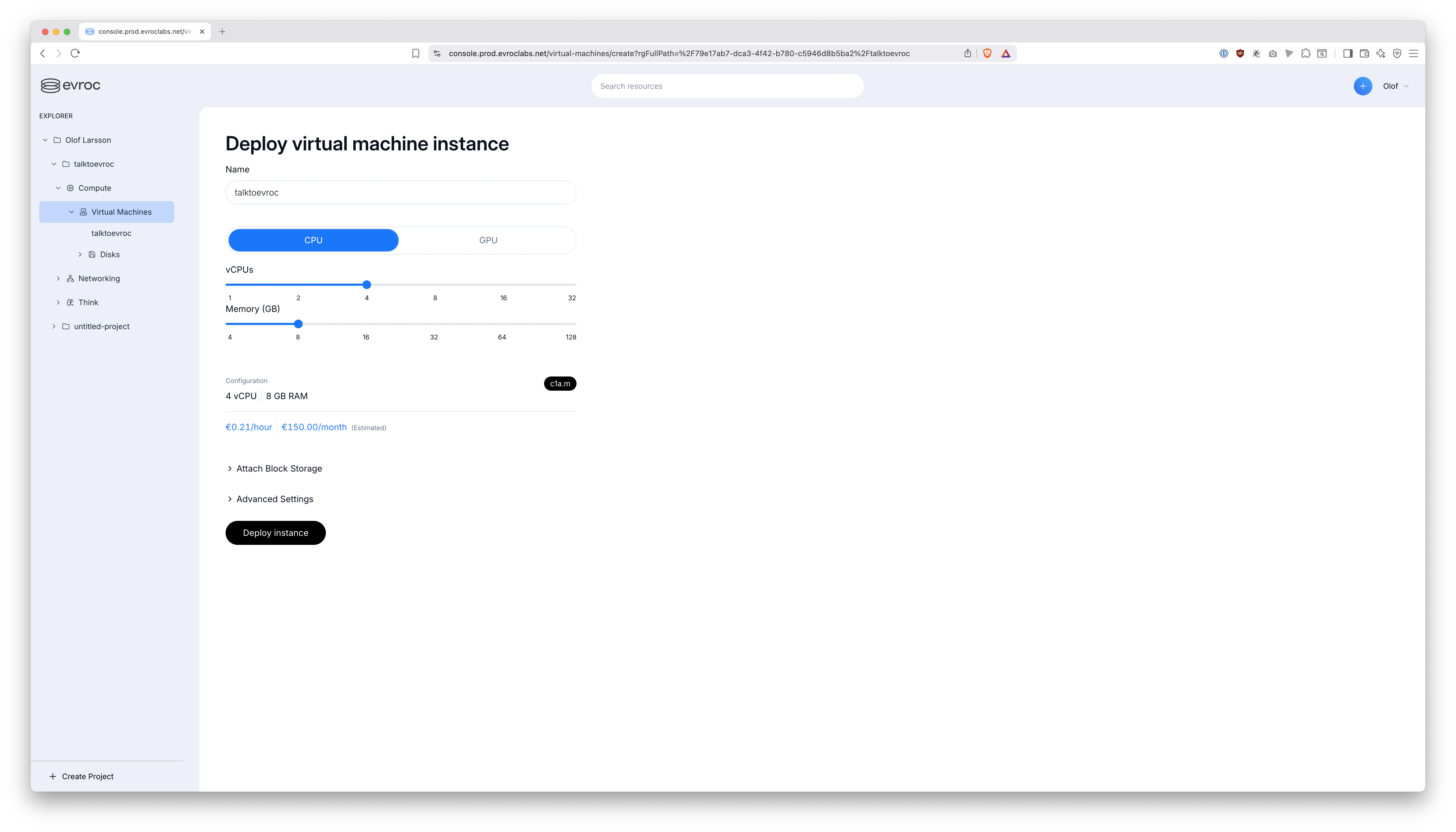
No need to "Attach Block Storage", because boot disk is 50 GB, which is enough.
Click the "Advanced Settings" and pick:
- Operating System: "ubuntu"
- Assign Public IP address: Yes, please
- Security Groups:
default-sto-1,default-sto-1-ssh,default-sto-1-web - SSH Key: Add your public key here
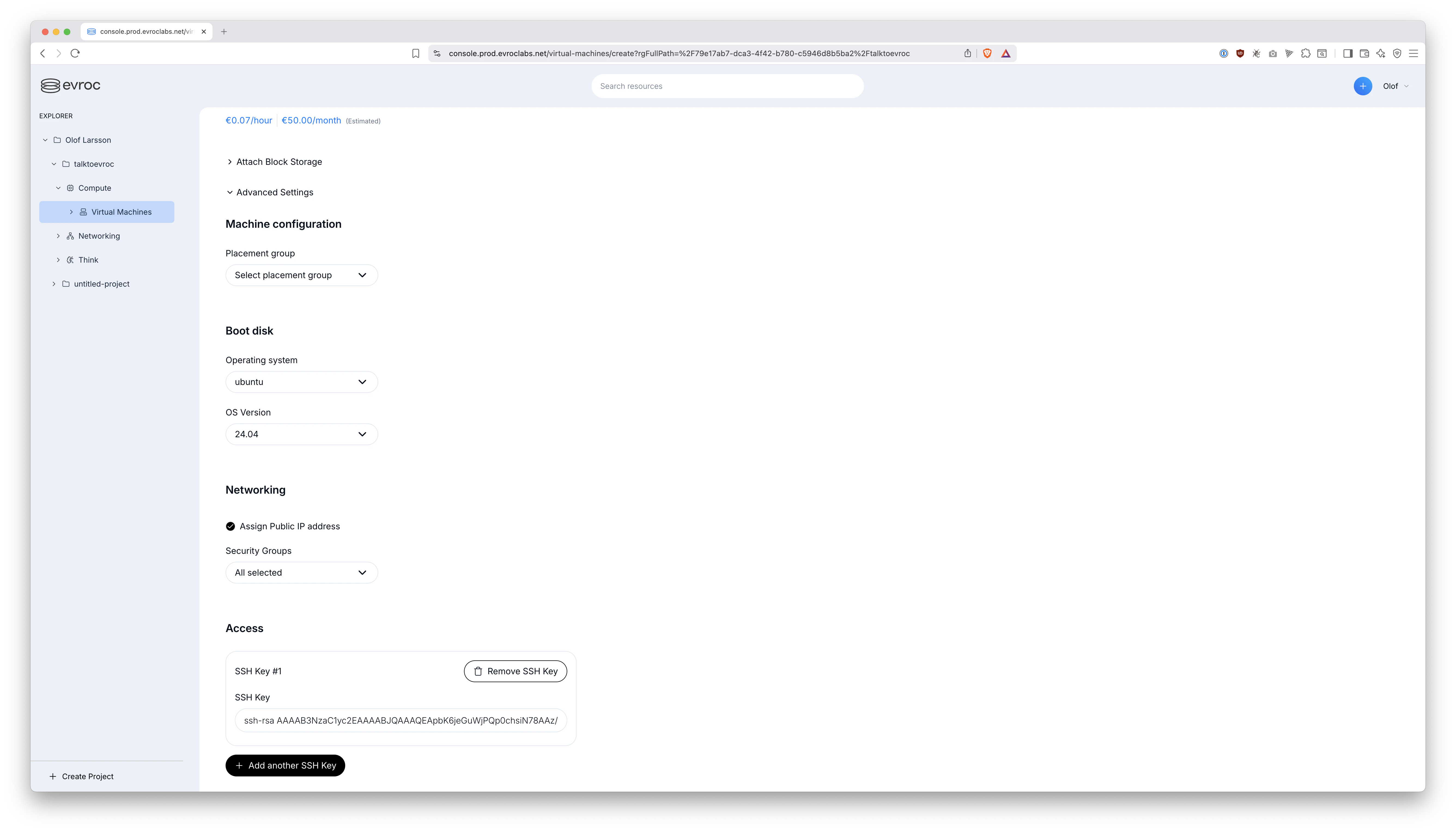
4️⃣ Then, click "Deploy instance".
- ⏳ The VM will take a minute or two to boot up.
- 🌐 You will now have a public IP. Point your domain name DNS there.
- ⌨️ Also make sure
ssh evroc-user@the-public-ipworks for you.
5️⃣ Finally, the time has come to deploy with https://kamal-deploy.org:
The user created for you is going to be called evroc-user. This section in https://github.com/oloflarsson/TalkToEvroc/blob/master/config/deploy.yml handles that:
ssh:
user: evroc-user
One manual step you must perform though since we are not running as root:
ssh evroc-user@the-public-ip
sudo usermod -a -G docker evroc-user
exit
I've obviously skimmed over the basics such as how to set DNS and use https://kamal-deploy.org here. Luckily, Kamal is way easier to learn than Kubernetes. If you are a smaller organization or just a single individual deploying hobby projects I can not recommend it enough. It creates SSL certificates etc for you automatically. Mostly just works out of the box!
💡 Room for improvement / What's next?
🗣️ Piper only offers "okay" text to speech quality. Here we are noticeably behind https://elevenlabs.io in quality. Evroc does not yet offer https://github.com/resemble-ai/chatterbox or similar more cutting edge TTS engines as part of their shared offering. Who knows, maybe one day they will!?
☎️ Talking with AI over regular phone seems like it would be natural next step. Luckily, PipeCat has built in support for that https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/telephony/overview. I have not tested it myself, so can not say for sure how hard the SIP trunk integration would be. Best of luck!
🎯 Conclusion
All the components we need are finally available to build completely Swedish 🇸🇪 realtime conversational voice agents with ease.
This was NOT the case a year ago:
KB Whisperwas released on February 20, 2025GPT-OSS-120Bwas released on August 5, 2025- Numerous improvements to https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat made during 2025
🇸🇪 And Finally: Evroc
- A Swedish owned company with Swedish datacenter - Truly Sovereign.
- Launching their PayGo AI API just now in 2026 - affordable as opposed to dedicated GPU offerings.
- Powered by Blackwell - just amazing performance.
- Because they support running regular VMs as well - you can have everything in the same datacenter for low latency.
🚀 Building realtime Swedish conversational AI has never been this doable in practice!
👀 If you haven't already, try it yourself: https://talktoevroc.olof.tech